Prognostic value of conventional and distinct restraint approaches for rumenotomy expressed by interleukin-1β and vital parameters in Kano-Brown goats
Keywords:
Ruminants, restraint, surgery, ELISA, cytokinesAbstract
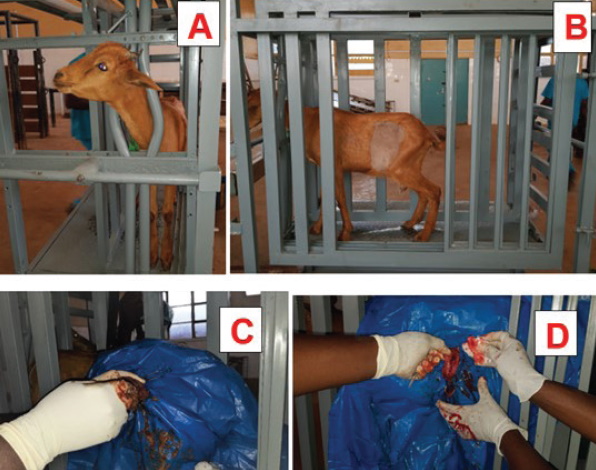
Lateral recumbency Rumen Skin Clamp Fixation (RSCF) and Stay Suture Rumenotomy (SSR) were compared to a
Standing Mobile Small Ruminant Surgical Chute (MSRSC) Rumenotomy, assessing the suitability of standing restraint for rumenotomy based on biomarkers of surgical stress in goats. Of 24 goats of both sexes, 18 KBGs diagnosed with rumen foreign bodies were allocated to groups A and B for lateral recumbency RSCF, SSR, and D for standing restraint MSRSC rumenotomy, respectively. Group C had six KBGs free of rumen foreign bodies. As vital parameters were recorded, blood was also drawn via jugular veins of each goat for sera and interleukin-1β (IL-1β) ELISA at Pre, and 0h, 5h, 24h, 48h, 72h, and weeks 1, 2, and 3 post-rumenotomy. Mean vital parameters between groups did not significantly (P > 0.05) differ. Post-rumenotomy IL-1β profiles significantly differed (P < 0.05) in females of group A at 72 h (37.28 ± 21.59 ng/L) over group D (10.56 ± 0.79ng/L). At week 1, males of group A had significantly (P < 0.05) higher values than those of groups B, C and D (10.83 ± 0.38, 11.62 ± 0.96 and 16.36 ± 1.54 ng/L). The absence of significant differences in the means of vital parameters suggests that the standing MSRSC rumenotomy did not differ in the severity of surgical stress over and above conventional lateral recumbency RSCF and SSR. In contrast, expressions of IL-1β demonstrate the superiority of the Standing Restraint Rumenotomy as the preferred approach.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Abubakar Mshelia Saidu, Samuel Tanko Fadason, Gabriel Enenche Ochube, Sani Adamu

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.







