Forensic meaning of Core temperature - An indicator for assessing the severity of heatstroke in an animal model
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.51607/22331360.2023.72.2.183Keywords:
Heat stroke, rats, temperature, variationAbstract
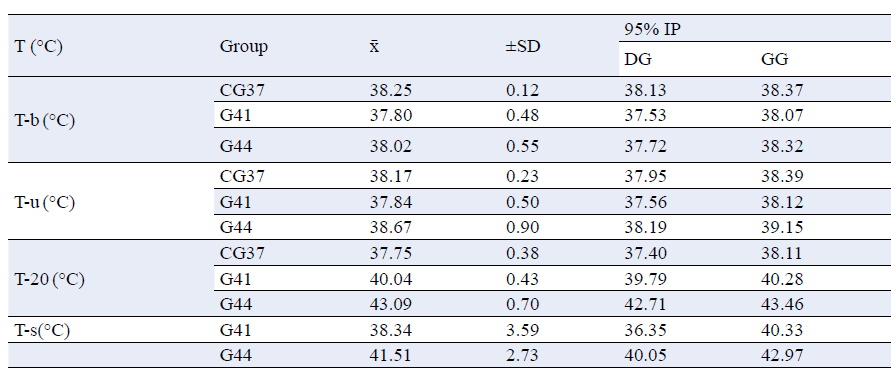
Sudden deaths during efforts that are multifactorial and associated with exposure of the body to high temperatures beyond the power of thermoregulatory mechanisms are increasingly common. Autopsies are often performed, but the evidence is insufficient and non-specific. The research is aimed to determine the core temperature values of rats exposed to different water temperatures (37°C, 41°C, 44°C), before the start of the experiment (Tb), after immersion in water (Tu), after 20 minutes of exposure and at death (Ts) in rats for hyperthermia and heat stroke. Forty rats were divided into five groups depending on the temperature and length of exposure to water: control group-CG37, G41-hyperthermia- group which exposure time was 20 minutes at 41°C, G41-heat stroke- group exposed until death at 41°C, G44- hyperthermia- group which exposure time was 20 minutes at 44°C, G44- heat stroke- group exposed until death at 44°C. A RET-4 probe was used to measure the core temperature of rats. Significant changes in the body temperature of rats were observed during the lethal outcome, p<0.0005. After exposure to water temperature for a period of 20 minutes, depending on the group, it was observed that the body temperatures of rats differed significantly between G37 and G41, CG37 and G44, p<0.0005 and G41 and G44, p<0.0005. A significant difference was also observed in the post mortem temperature of groups G41 and G44, p=0.01, a significant difference between body temperatures in groups CG37, G41-hyperthermia, G41- heat stroke, G44-hyperthermia and G44-heat stroke (p<0.0005), and the significance of the differences in the CG37 group was p=0.044. Exposure of albino rats to different water temperatures also led to the changes in the internal temperature; normothermia was established through thermoregulation in the control group, and in the other groups, hyperthermia and heat stress occurred.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Emina Dervišević, Lejla Dervišević, Zurifa Ajanović, Aida Bešić, Adis Salihbegović, Ekrema Mujarić, Muamer Dervišević

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.







