Novel atherogenic indices and risk of cardiovascular complications in patients of hypertension
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.51607/22331360.2025.74.3.249Keywords:
Atherogenic dyslipidemia, cardiovascular risk, hypertensionAbstract
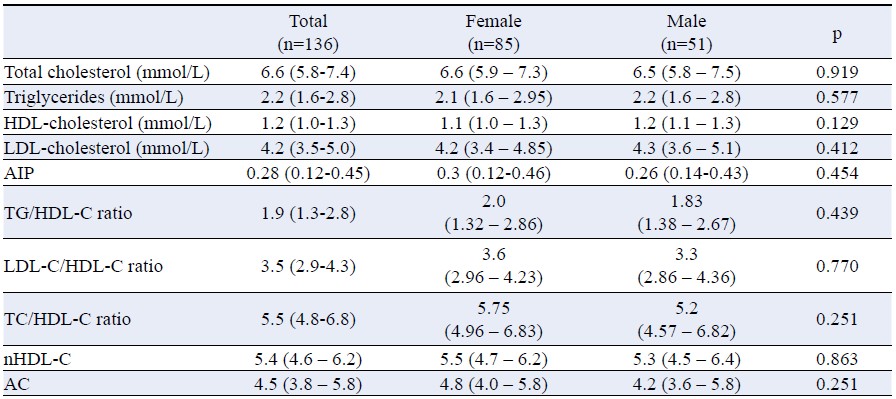
The study was aimed to evaluate the lipid panel parameters in Hypertension (HTA) patients along with gender-dependent comparison and Cardiovascular Disease (CVD) risk estimated based on Atherogenic Index of Plasma (AIP) values. This study aims to emphasize the importance of the lipid profile in blood in cardiovascular patients with hypertension. Total number of 136 adult HTA patients (85 female/51 male; mean age 63.3 ± 10.2 years old) were incorporated in this retrospective study. According to CVD risk estimated based on AIP values, patients were classified into two groups: HTA patients with low/moderate CVD risk - AIP ≤ 0.21 (n=51) and HTA patients with high CVD risk - AIP >0.21 (n=85). Triglycerides (TG), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (nHDL-C), total cholesterol (TC), Atherogenic coefficient (AC), TG/HDL-C ratio, LDL-C/HDL-C ratio and TC/HDL-C ratio were used for comparison of both groups. Routine lipid parameters were analysed by standard biochemical methods. For calculation of composite lipid indices, we used reference formulas. HTA patients with high CVD risk had significantly higher levels of TC (p=0.02), TG/HDL-C ratio, TG, AIP, LDL-C/HDL-C ratio, nHDL-cholesterol, TC/HDL-C ratio, and atherogenic coefficient, and significantly lover HDL-C compared to HTA patients with low/moderate CV risk (p<0.001 respectively). Our findings underscore the importance of considering various lipid profile parameters in risk stratification among patients with HTA.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Emina Dervišević, Lejla Čolak, Amela Dervišević, Zurifa Ajanović, Ekrema Mujarić, Aida Bešić, Ferid Krupić, Edina Lazović, Hajrudin Spahović, Nedim Šuta, Almir Fajkić

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.







